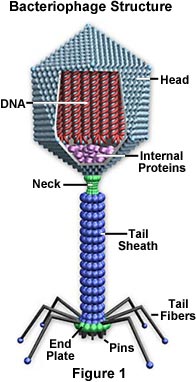
bacteriophage: category of viruses that affect bacterial cell.
cloning: making an identical copy of DNA of an organism.
cytosine: one of nitrogen containing bases in nucleotide.
DNA: molecule of inheritance
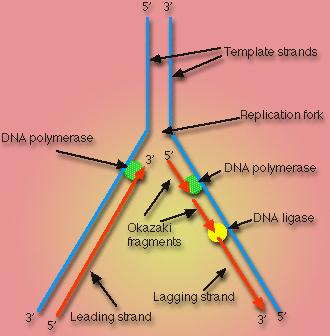
DNA ligase: Enzymes that seal new base pairing during DNA replication
DNA polymerase: enzymes of replication and repair that assembles new DNA or an DNA template
DNA repair: enzymes that fixes small scale alterations a DNA strand
DNA replication: any process were cell duplicates its DNA before dividing
guanine: nitrogen containig base in one of four nucleotide monomers of DNA or RNA
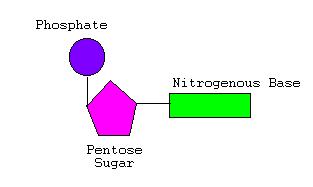
nucleotide: small organic compounds with deoxybirose and phosphate group
thymine: one of nucleotide in DNA.
x-ray diffraction image: pattern that forms on films exposed x ray that have been directed al moleculeanticodon: series of three nucleotide bases in RNA
base sequence: sequencial order of bases in DNA or RNA strand
base pair sustitution: one amino acid replaced another during protein synthases.
carcinogen: any substances or agent that can trigger cancer
codon: one of 64 possible base tripets inan RNA strand
deletion: loss of a segment from a chromosome
exon: one of base sequence of RNA transcript that will become translated
intron: noncoding portion of a pre-RNA transcript
gene mutation: small scale change in nucleotide sequence of DNA molecule
genetic code: correspondence between one of a few bases into DNA strand
insertion: insertion of one of a few bases into DNA strand
ioning: high energy wavelenght
mRNA: single strand of nibonucleotide transcribed from DNA them to poipeptide chains.
mutation rate: probability that a spontaneous mutation will occur during DNA replication.


















No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario